
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Ultrafast Laser Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, School of Precision Instruments and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Science and Technology on Electro-Optical Information Security Control Laboratory, Tianjin 300308, China
As a newly discovered type of structured light, a spatiotemporal optical vortex (STOV), which is remarkable for its space–time spiral phase and transverse orbital angular momentum (OAM), has garnered substantial interest. Most previous studies have focused on the generation, characterization, and propagation of STOVs, but their nonlinear frequency conversion remains largely unexplored. Here, we experimentally demonstrate the generation of green and ultraviolet (UV) STOVs by frequency upconversion of a STOV carried near-infrared (NIR) pulse emitted by a high repetition rate Yb-doped fiber laser amplifier system. First, we verify that the topological charge of spatiotemporal OAM (ST-OAM) is doubled along with the optical frequency in the second-harmonic generation (SHG) process, which is visualized by the diffraction patterns of the STOVs in the fundamental and second-harmonic field. Second, the space–time characteristic of NIR STOV is successfully mapped to UV STOV by sum-frequency mixing STOV at 1037 nm and Gaussian beams in the green band. Furthermore, we observe the topological charges of the ST-OAM could be degraded owing to strong space–time coupling and complex spatiotemporal astigmatism of such beams. Our results not only deepen our understanding of nonlinear manipulation of ST-OAM spectra and the generation of STOVs at a new shorter wavelength, but also may promote new applications in both classical and quantum optics.
ultraviolet spatiotemporal optical vortex second-harmonic generation sum-frequency generation Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(8): 080004
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Ultrafast Laser Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, School of Precision Instruments and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Georgia Tech Shenzhen Institute (GTSI), Tianjin University, Shenzhen 518067, China
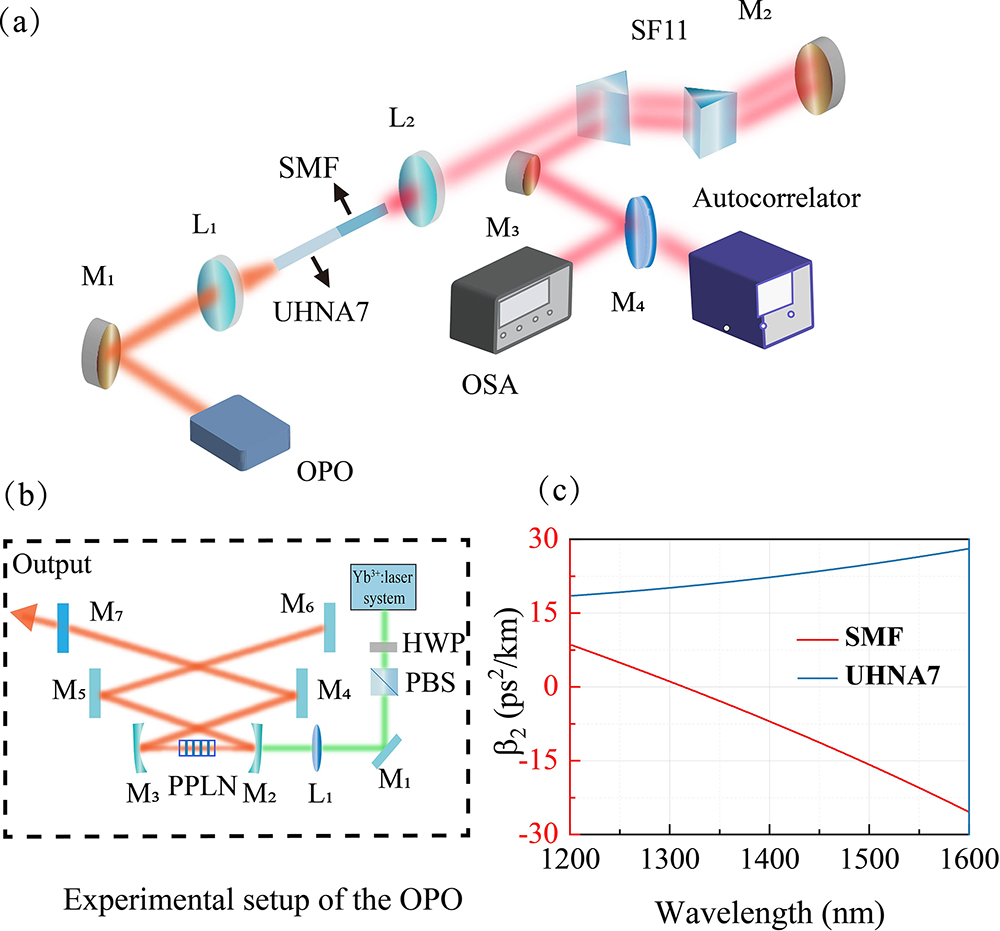
We report an experimental generation of few-cycle pulses at 53 MHz repetition rate. Femtosecond pulses with pulse duration of 181 fs are firstly generated from an optical parametric oscillator (OPO). Then, the pulses are compressed to sub-three-cycle with a hybrid compressor composed of a commercial single-mode fiber and a pair of prisms, taking advantage of the tunability of the OPO and the numerical simulating of the nonlinear compression system. Our compressed optical pulses possess an ultrabroadband spectrum covering over 470 nm bandwidth (at ), and the output intensity fluctuation of our system is less than 0.8%. These results show that our system can effectively generate few-cycle pulses at a repetition rate of tens of megahertz with excellent long-term stability, which could benefit future possible applications.
nonlinear compression few cycle pulse optical parametric oscillator Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(5): 051901
天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院超快激光研究室&光电信息技术教育部重点实验室, 天津 300072
超快光学参量振荡器(OPOs)是获得高重复频率、高平均功率、宽光谱调谐脉冲输出的理想途径,为化学、生物、纳米光子学等领域的研究提供了强有力的手段。随着掺Yb 3+光纤飞秒激光器输出功率的不断提升及非线性晶体制备工艺的成熟,Yb光纤激光器泵浦的飞秒OPOs发展势头变得锐不可挡。回顾了近年来光纤飞秒激光器泵浦的OPOs的研究进展,介绍了利用飞秒OPOs拓宽波长覆盖范围、提升脉冲重复频率、获得少周期脉冲产生、实现结构光场输出的具体技术方案。最后介绍了飞秒OPOs在纳米光子学、拉曼光谱技术领域的应用。
非线性光学 光学参量振荡器 光纤飞秒激光器 少周期脉冲 结构光场 纳米光子学 中国激光
2021, 48(19): 1901001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Quantum Optics, Leibniz University Hannover, Welfengarten 1, D-30167 Hannover, Germany
2 Cluster of Excellence PhoenixD, Welfengarten 1, D-30167 Hannover, Germany
3 neoLASE GmbH, Hollerithallee 17, D-30419 Hannover, Germany
Ultrafast visible radiation is of great importance for many applications ranging from spectroscopy to metrology. Because some regions in the visible range are not covered by laser gain media, optical parametric oscillators offer an added value. Besides a high-power broadband laser source, the ability to rapidly tune the frequency of pulses with high-power spectral density offers an extra benefit for experiments such as multicolor spectroscopy or imaging. Here, we demonstrate a broadband, high-power, rapidly tunable femtosecond noncollinear optical parametric oscillator with a signal tuning range of 440–720 nm in the visible range. The oscillator is pumped by the third harmonic of an Yb-fiber laser at 345 nm with a repetition rate of 50.2 MHz. Moreover, the signal wavelength is tuned by changing the cavity length only, and output powers up to 452 mW and pulse durations down to 268 fs are achieved. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first demonstration of a quickly tunable femtosecond optical parametric oscillator that covers nearly the entire visible spectral range with high output power.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(9): 09001715
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Ultrafast Laser Laboratory, Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, School of Precision Instruments and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Institut für Quantenoptik, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Welfengarten 1, 30167 Hannover, Germany
3 Cluster of Excellence PhoenixD (Photonics, Optics, and Engineering-Innovation Across Disciplines), 30167 Hannover, Germany
4 Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V., Hollerithallee 8, 30419 Hannover, Germany
5 e-mail: yjsong@tju.edu.cn
6 e-mail: huminglie@tju.edu.cn
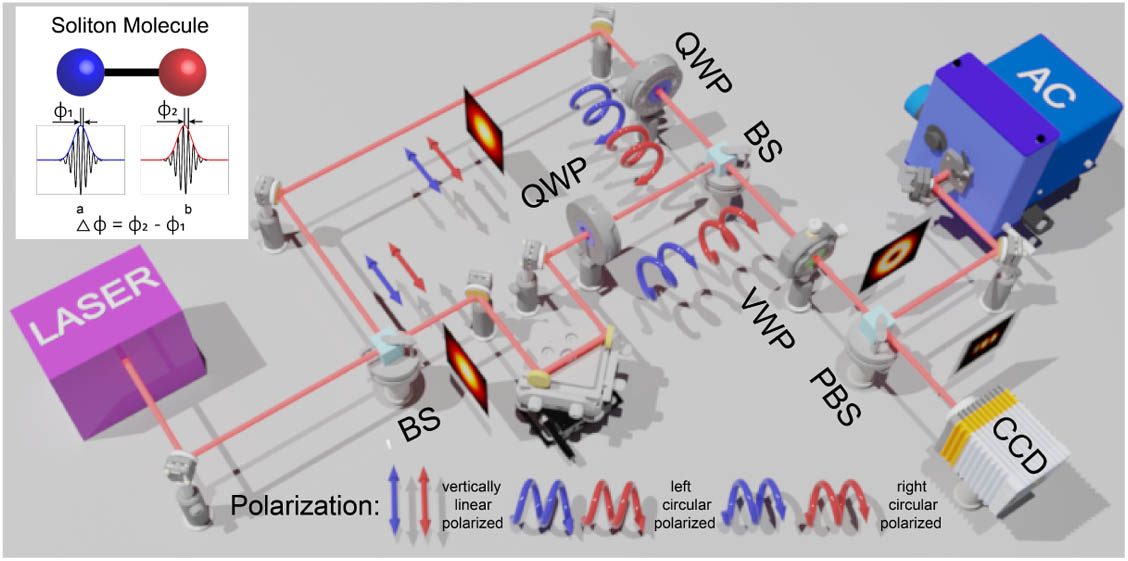
Internal motions in femtosecond soliton molecules provide insight into universal collective dynamics in various nonlinear systems. Here we introduce an orbital-angular-momentum (OAM)-resolved method that maps the relative phase motion within a femtosecond soliton molecule into the rotational movement of the interferometric beam profile of two optical vortices. By this means, long-term relative phase evolutions of doublet and triplet soliton molecules generated in an all-polarization-maintaining mode-locked Er-fiber laser are revealed. This simple and practical OAM-resolved method represents a promising way to directly visualize the complex phase dynamics in a diversity of multisoliton structures.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(10): 10001580

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Tianjin University, College of Precision Instrument and Optoelectronics Engineering, Ultrafast Laser Laboratory, Tianjin, China
2 Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Quantenoptik, Hannover, Germany
3 Cluster of Excellence PhoenixD (Photonics, Optics, and Engineering-Innovation Across Disciplines), Hannover, Germany
Optical vortices, which carry orbital angular momentum, offer special capabilities in a host of applications. A single-laser source with dual-beam-mode output may open up new research fields of nonlinear optics and quantum optics. We demonstrate a dual-channel scheme to generate femtosecond, dual-wavelength, and dual-beam-mode tunable signals in the near infrared wavelength range. Dual-wavelength operation is derived by stimulating two adjacent periods of a periodically poled lithium niobate crystal. Pumped by an Yb-doped fiber laser with a Gaussian (lp = 0) beam, two tunable signal emissions with different beam modes are observed simultaneously. Although one of the emissions can be tuned from 1520 to 1613 nm with the Gaussian (ls = 0) beam, the other is capable of producing a vortex spatial profile with different vortex orders (ls = 0 to 2) tunable from 1490 to 1549 nm. The proposed system provides unprecedented freedom and will be an exciting platform for super-resolution imaging, nonlinear optics, multidimensional quantum entanglement, etc.
nonlinear optics parametric processes optical parametric oscillators ultrafast nonlinear optics Advanced Photonics
2020, 2(4): 045001
天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院光电信息技术教育部重点实验室, 天津 300072
设计并搭建了可调谐飞秒光学参量振荡系统, 研究了不同腔长处信号光的稳定性, 通过比例积分控制系统控制腔长, 分别利用功率锁定和波长锁定两种方法提升了系统的信号光输出稳定性, 对比了两种方法分别对信号光输出功率和光谱稳定性的提升效果, 研究了两种锁定方式的锁定特点。实验中, 利用光纤飞秒激光器抽运PPLN晶体, 实现了信号光中心波长在1317~1610 nm连续调谐。通过功率锁定, 将15 min内信号光的功率稳定性提升至0.16%, 波长稳定性提升至0.35%; 通过波长锁定, 将15 min内信号光的功率稳定性提升至0.25%, 波长稳定性提升至0.03%, 利用两种方法都实现了信号光输出功率和波长稳定性的提升。不同的应用领域对于飞秒光学参量振荡器输出信号光功率稳定性及光谱稳定性有不同的要求, 本研究对比了两种锁定方式的锁定效果, 为今后相关研究提供了实验依据与参考。
激光器 非线性光学 光学参量振荡器 比例积分控制系统 飞秒激光 同步抽运 中国激光
2018, 45(10): 1001006
天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院超快激光研究室, 光电信息技术教育部重点实验室, 天津 300072
最近十几年来,随着飞秒激光技术及非线性晶体制备技术的逐渐成熟,非线性光学频率变换技术得到了飞速发展。非线性光学频率变换技术的研究旨在突破激光增益介质发射谱线的限制,使激光器输出波长拓展至传统激光器所无法直接输出的波段范围,以满足更加广泛的科研及应用需求。到目前为止,非线性频率变换技术是获得多波长和可调谐飞秒激光的最简捷有效的途径。近些年来,本研究室在研究光纤飞秒激光器的基础上,开展了基于掺Yb
3+光子晶体光纤飞秒激光系统抽运不同介质的非线性频率变换研究,主要包括:基于块状晶体的光学参量振荡(OPO)技术、基于砷化镓(GaAs)纳米线的频率上转换、基于高非线性光子晶体光纤的超连续谱及三次谐波的产生。简要介绍国内外相关研究成果,重点综述了本研究室近五年来在上述研究领域的科研成果,分别介绍了OPO技术、砷化镓(GaAs)纳米线的频率上转换和基于高非线性光子晶体光纤的超连续谱及三次谐波的产生技术的基本原理、研究进展以及前沿应用。
非线性光学 非线性光学频率变换 光子晶体光纤飞秒激光 光学参量振荡器 砷化镓纳米线 高非线性光子晶体光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(4): 040001
天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院超快激光研究室, 天津 300072
三硼酸锂(LBO)具有良好的非线性光学特性和极其稳定的物化性能,其色散量对晶体温度变化敏感,是可实现非临界相位匹配的优良的非线性光学晶体。报道了高功率绿光飞秒激光同步抽运以三硼酸锂(LBO)为非线性晶体的单共振光学参量振荡器(OPO)。抽运源为高平均功率大模场面积掺镱光子晶体光纤飞秒激光器放大级的输出飞秒光的锁模倍频激光,通过调节晶体温度,采用非临界相位匹配方式,获得了红光至近红外光可调谐的高功率飞秒激光,OPO的信号光调谐范围为670~880 nm,相应闲频光在2320~1270 nm范围内可调。在3.4 W抽运功率下,中心波长为694 nm的信号光输出获得最高平均功率为660 mW,脉冲宽度为132 fs,转换效率为19.4%。
非线性光学 光学参量振荡器 三硼酸锂 光纤飞秒激光器





